Featured publications
![]() Evans K. S., M. H. van Wijk, P. T. McGrath, E. C. Andersen, and M. G. Sterken, 2021 From QTL to gene: C. elegans facilitates discoveries of the genetic mechanisms underlying natural variation. Trends Genet.
Evans K. S., M. H. van Wijk, P. T. McGrath, E. C. Andersen, and M. G. Sterken, 2021 From QTL to gene: C. elegans facilitates discoveries of the genetic mechanisms underlying natural variation. Trends Genet.
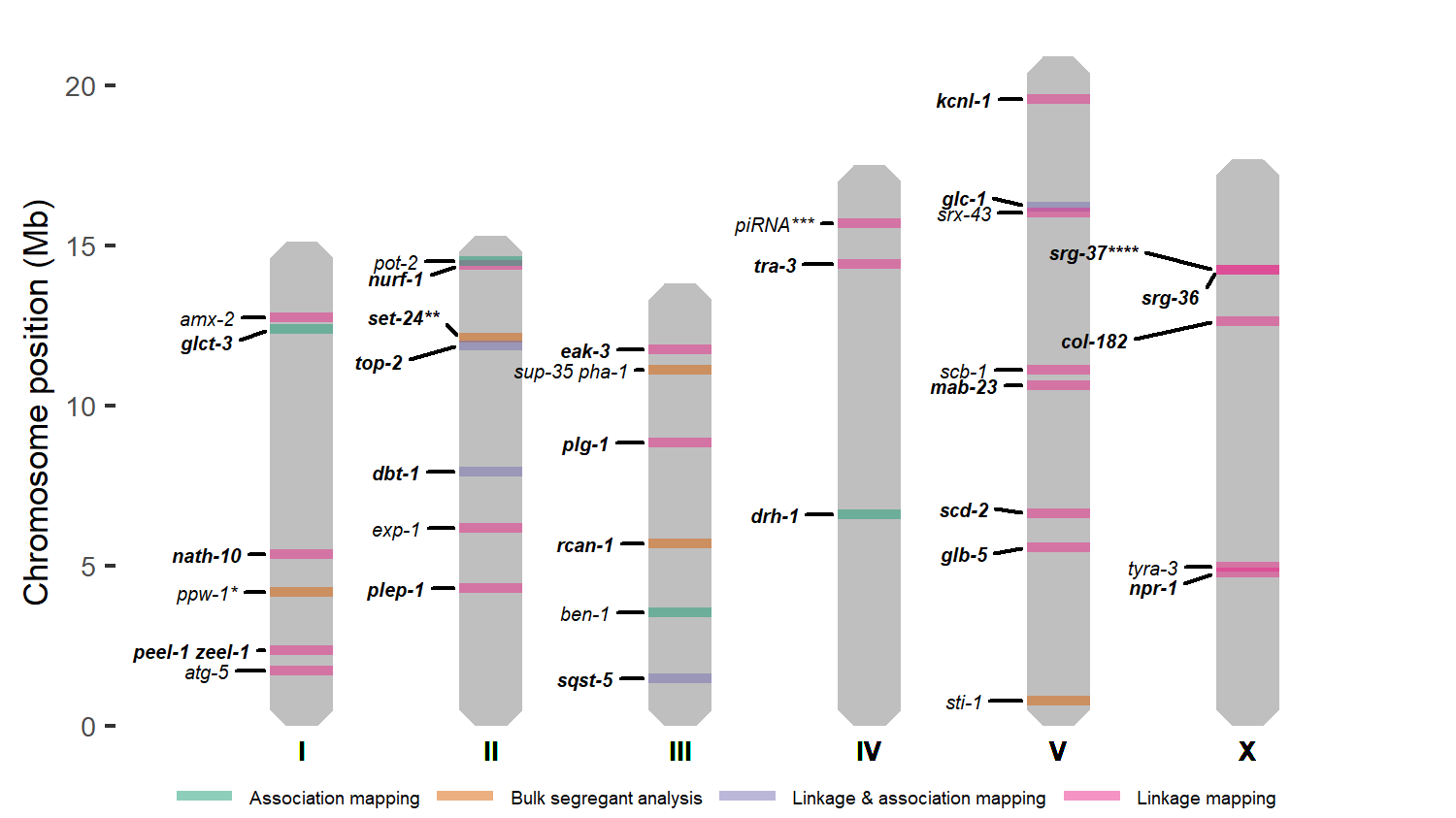
- Innovations in quantitative trait loci mapping and genome editing have led to the discovery and validation of 37 genes and variants underlying phenotypic variation in C. elegans.
- Numerous recombinant panels and a large collection of wild strains make C. elegans a formidable model to understand quantitative trait variation.
- Most of the identified quantitative trait genes have paralogs, providing evidence that gene duplication events are important for shaping quantitative traits.
- Pleiotropy is relatively common among C. elegans quantitative trait genes.
![]() Evans K. S., S. Zdraljevic, L. Stevens, K. Collins, R. E. Tanny, et al., 2020 Natural variation in the sequestosome-related gene, sqst-5, underlies zinc homeostasis in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 16: e1008986.
Evans K. S., S. Zdraljevic, L. Stevens, K. Collins, R. E. Tanny, et al., 2020 Natural variation in the sequestosome-related gene, sqst-5, underlies zinc homeostasis in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 16: e1008986.
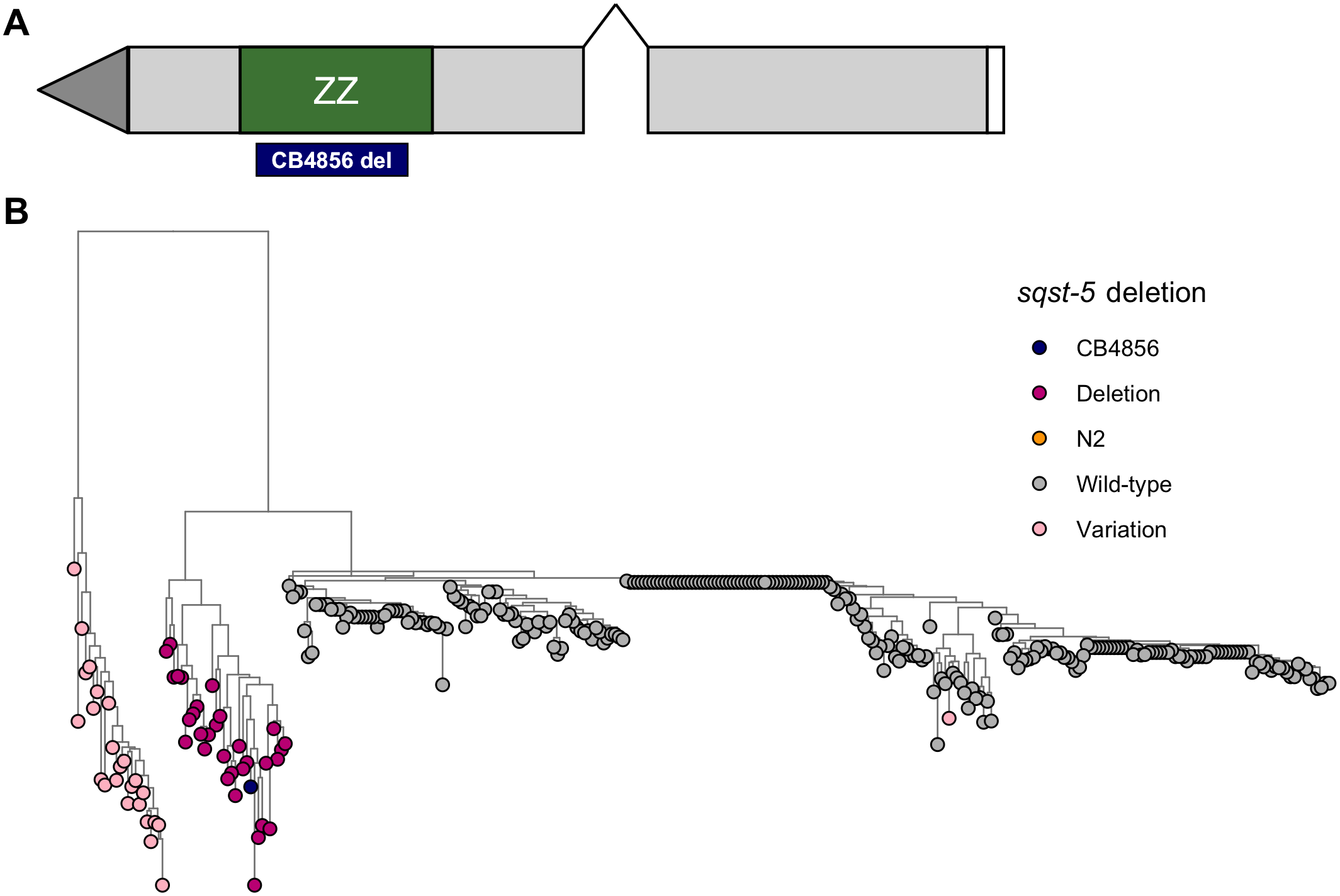
- Zinc, although an essential metal, can be toxic if organisms are exposed to concentrations that are too high or too low
- Using linkage mapping in C. elegans, we identified four loci (including the sqst-5 locus) that contributed to differential zinc responses
- Although SQST-5 contains a conserved zinc-binding protein domain, we were the first to directly implicate it in the C. elegans zinc response pathway
- Our results offer a possible mechanism for how organisms can respond to naturally high levels of zinc in the environment and how zinc homeostasis varies among individuals
![]() Evans K. S., J. Wit, L. Stevens, S. R. Hahnel, B. Rodriguez, et al., 2021 Two novel loci underlie natural differences in Caenorhabditis elegans abamectin responses. PLoS Pathog. 17: e1009297.
Evans K. S., J. Wit, L. Stevens, S. R. Hahnel, B. Rodriguez, et al., 2021 Two novel loci underlie natural differences in Caenorhabditis elegans abamectin responses. PLoS Pathog. 17: e1009297.
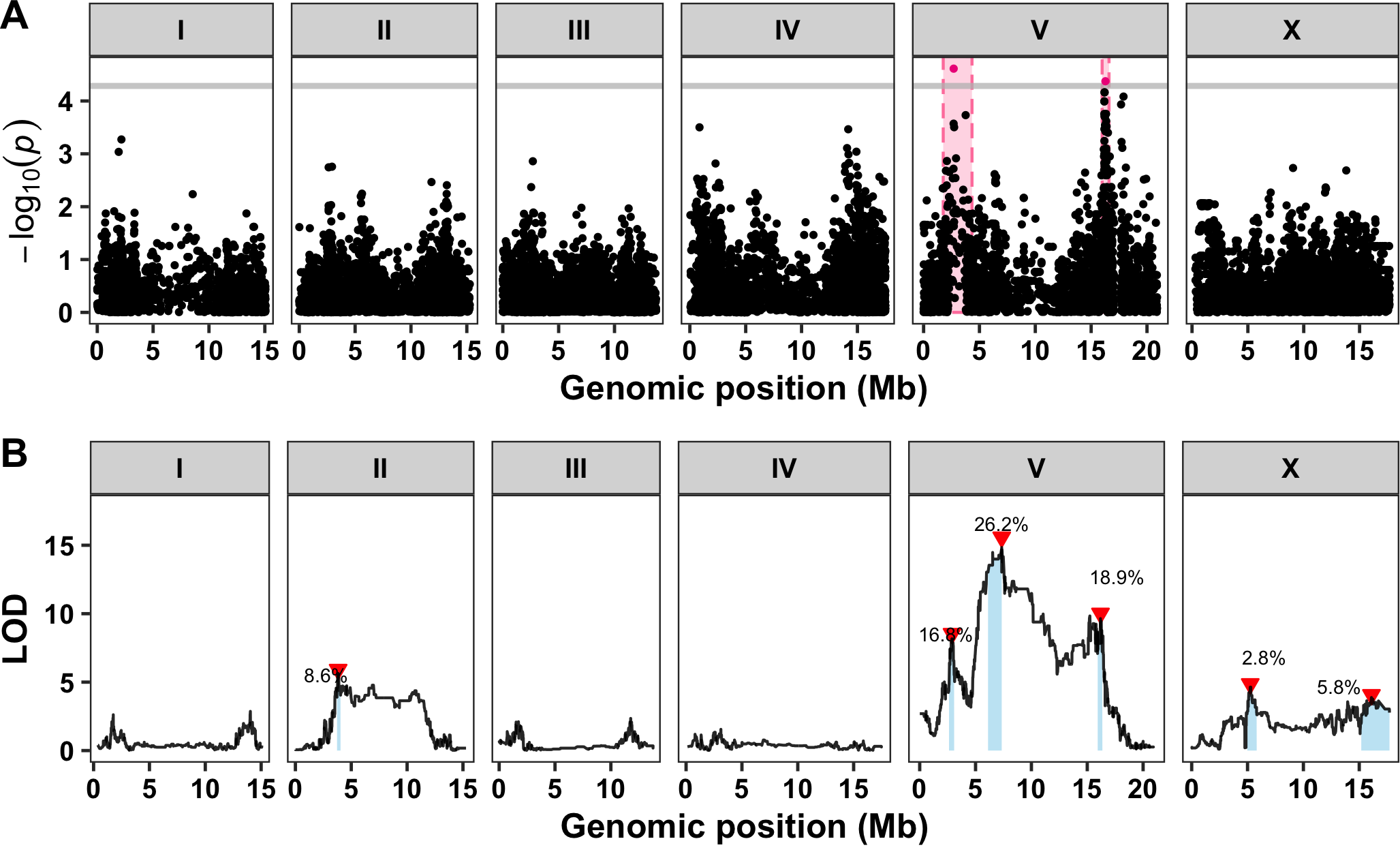
- Parasitic nematode infections are a major world-wide threat and resistance to anthelmintic treatments is rampant
- We identified three loci on chromosome V that contribute to differential responses to the anthelmintic abamectin
- Candidate gene comparison between resistance loci in C. elegans and the parasite Haemonchus contortus found several cases of overlap between the two species
- This study highlights the advantages of using C. elegans to understand anthelmintic resistance in parasitic nematodes
All publications
2022
Webster A. K., R. Chitrakar, M. Powell, J. Chen, K. Fisher, Evans K. S., et al., 2022 Using population selection and sequencing to characterize natural variation of starvation resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. eLife.
Widmayer S. J., K. Evans, S. Zdraljevic, and E. C. Andersen, 2022 Evaluating the power and limitations of genome-wide association studies in C. elegans. G3.
Crombie T. A., P. Battlay, R. E. Tanny, K. S. Evans, C. M. Buchanan, et al., 2022 Local adaptation and spatiotemporal patterns of genetic diversity revealed by repeated sampling of Caenorhabditis elegans across the Hawaiian Islands. Mol. Ecol.
2021
Evans K. S., M. H. van Wijk, P. T. McGrath, E. C. Andersen, and M. G. Sterken, 2021 From QTL to gene: C. elegans facilitates discoveries of the genetic mechanisms underlying natural variation. Trends Genet.
Evans K. S., J. Wit, L. Stevens, S. R. Hahnel, B. Rodriguez, et al., 2021 Two novel loci underlie natural differences in Caenorhabditis elegans abamectin responses. PLoS Pathog. 17: e1009297.
2020
Evans K. S. 2020 Investigating the Genetic Mechanisms of Phenotypic Variation in Caenorhabditis elegans. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing.
Evans K. S., S. Zdraljevic, L. Stevens, K. Collins, R. E. Tanny, et al., 2020 Natural variation in the sequestosome-related gene, sqst-5, underlies zinc homeostasis in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet. 16: e1008986.
Evans K. S., and E. C. Andersen, 2020b The cadmium-responsive gene, cdr-6, does not influence Caenorhabditis elegans responses to exogenous zinc. microPublication Biology 2020.
Evans K. S., and E. C. Andersen, 2020a The Gene scb-1 Underlies Variation in Caenorhabditis elegans Chemotherapeutic Responses. G3.
2019
Crombie T. A., S. Zdraljevic, D. E. Cook, R. E. Tanny, S. C. Brady, K. S. Evans, et al., 2019 Deep sampling of Hawaiian Caenorhabditis elegans reveals high genetic diversity and admixture with global populations. Elife 8: e50465.
Kim C., J. Kim, S. Kim, D. E. Cook, K. S. Evans, et al., 2019 Long-read sequencing reveals intra-species tolerance of substantial structural variations and new subtelomere formation in C. elegans. Genome Res. 29: 1023–1035.
2018
Evans K. S., S. C. Brady, J. S. Bloom, R. E. Tanny, D. E. Cook, et al., 2018 Shared Genomic Regions Underlie Natural Variation in Diverse Toxin Responses. Genetics.
2017
Currie S. L., J. J. Doane, K. S. Evans, N. Bhachech, B. J. Madison, et al., 2017 ETV4 and AP1 transcription factors form multivalent interactions with three sites on the MED25 activator-interacting domain. J. Mol. Biol.
Evans K. S., Y. Zhao, S. C. Brady, L. Long, P. T. McGrath, et al., 2017 Correlations of Genotype with Climate Parameters Suggest Caenorhabditis elegans Niche Adaptations. G3 7: 289–298.